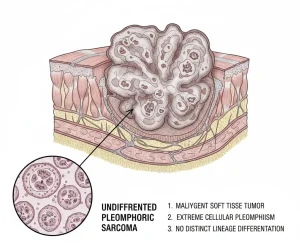
Overview
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma is a rare and aggressive type of soft tissue cancer that develops from connective tissues such as muscle, fat, fibrous tissue, or blood vessels. It was previously known as malignant fibrous histiocytoma. The tumor is called undifferentiated because the cancer cells do not resemble normal mature cells under a microscope, making the exact tissue of origin unclear. This cancer most commonly affects adults and usually develops in the arms, legs, or trunk, but it can occur anywhere in the body.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the tumor’s size and location. In the early stages, undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma may cause few or no noticeable signs.
Common symptoms may include:
-
A painless lump or swelling that gradually increases in size
-
Pain or tenderness if the tumor presses on nerves or muscles
-
Limited movement when the tumor is near a joint
-
Swelling in the affected limb
-
Fatigue or unexplained weight loss in advanced cases
Tumors located deep within tissues may grow quite large before being detected.
Causes
The exact cause of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma is not fully understood. It is believed to develop due to genetic mutations that cause cells to grow uncontrollably.
Possible contributing factors include:
-
Random genetic changes in soft tissue cells
-
Previous radiation therapy to the affected area
-
Long-term exposure to certain chemicals
-
Chronic tissue injury or inflammation, in rare cases
Most cases occur without a clearly identifiable cause.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma.
Risk factors include:
-
Increasing age, most commonly affecting adults over 50
-
Prior radiation therapy for another cancer
-
Exposure to industrial chemicals such as herbicides or dioxins
-
Certain inherited genetic syndromes, though this is uncommon
-
History of chronic lymphedema
Having one or more risk factors does not guarantee that the condition will develop.
Complications
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma can be aggressive and may lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
Possible complications include:
-
Local tissue destruction due to tumor growth
-
Recurrence of the cancer after treatment
-
Spread of cancer to other parts of the body, especially the lungs
-
Impaired function of affected muscles or joints
-
Complications related to surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy
Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment improve outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Prevention
There is no proven way to prevent undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, as most cases occur without a known cause. However, certain steps may help lower overall cancer risk or support early detection.
Preventive measures may include:
-
Limiting unnecessary exposure to radiation
-
Following safety guidelines when handling industrial chemicals
-
Seeking medical evaluation for any persistent or growing soft tissue lump
-
Attending regular follow-up appointments after radiation therapy or cancer treatment
Prompt medical attention for suspicious masses allows for earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
Advertisement