Overview
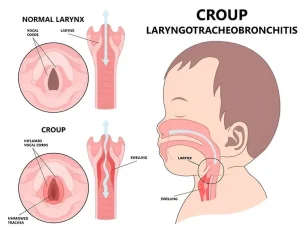
Croup is a common respiratory illness in young children that causes swelling of the upper airway, particularly around the voice box and windpipe. This swelling leads to a distinctive barking cough and hoarse voice. Croup is usually caused by a viral infection and is most common in infants and toddlers between 6 months and 3 years of age. Symptoms often worsen at night and typically improve within a few days.
Symptoms
Croup symptoms usually begin as a mild upper respiratory infection and progress as airway swelling increases.
Common symptoms include:
-
Barking cough that sounds like a seal
-
Hoarse or raspy voice
-
Noisy or high-pitched breathing, especially when inhaling
-
Runny nose or nasal congestion
-
Fever
-
Symptoms that worsen at night
-
Breathing difficulty in more severe cases
Children may appear anxious or restless when breathing becomes difficult.
Causes
Croup is most commonly caused by viral infections that affect the upper airway.
Common causes include:
-
Parainfluenza viruses
-
Influenza virus
-
Respiratory syncytial virus
-
Adenovirus
-
Measles virus in rare cases
The infection leads to inflammation and narrowing of the airway, which causes the characteristic cough and breathing sounds.
Risk factors
Certain children are more likely to develop croup.
Risk factors include:
-
Age between 6 months and 3 years
-
History of croup or recurrent respiratory infections
-
Seasonal occurrence, especially in fall and early winter
-
Exposure to viral infections in childcare settings
-
Lack of immunity to common respiratory viruses
Croup can occur in older children, but symptoms are usually milder.
Complications
Most cases of croup are mild, but complications can occur in severe or untreated cases.
Possible complications include:
-
Severe breathing difficulty
-
Low oxygen levels
-
Dehydration due to difficulty feeding
-
Secondary bacterial infections
-
Hospitalization in severe cases
Prompt medical attention is important if breathing problems worsen.
Prevention
Croup cannot always be prevented, but steps can reduce the risk of viral infections.
Preventive measures include:
-
Frequent handwashing
-
Avoiding close contact with sick individuals
-
Keeping children’s vaccinations up to date
-
Cleaning shared toys and surfaces regularly
-
Teaching children proper cough and sneeze hygiene
Early recognition and appropriate care help ensure quick recovery and prevent complications.
Advertisement